Water Treatment Plant - Ignition
Building a Water Treatment Plant Simulator in Ignition with Python & OPC UA
I recently completed a major milestone in my water treatment plant simulation project, using Ignition by Inductive Automation as the visualization platform and Python to simulate real-time OPC UA data. This project has been a fantastic way to learn both industrial automation concepts and the power of Ignition for rapid prototyping.
Project Overview
The goal was to create a realistic, interactive water treatment plant dashboard in Ignition, powered by simulated data from a Python OPC UA server. This allowed me to experiment with plant operations, alarms, and trends—all without needing physical hardware.
Why Simulate?
Industrial automation platforms like Ignition are powerful, but real-world data isn’t always available for learning and prototyping. By simulating a water treatment plant, I was able to explore Ignition’s features—dashboards, alarms, historical trends, and more—using realistic, dynamic data.
How It Works
I wrote a Python script that acts as an OPC UA server, hosting variables for each stage of the water treatment process:
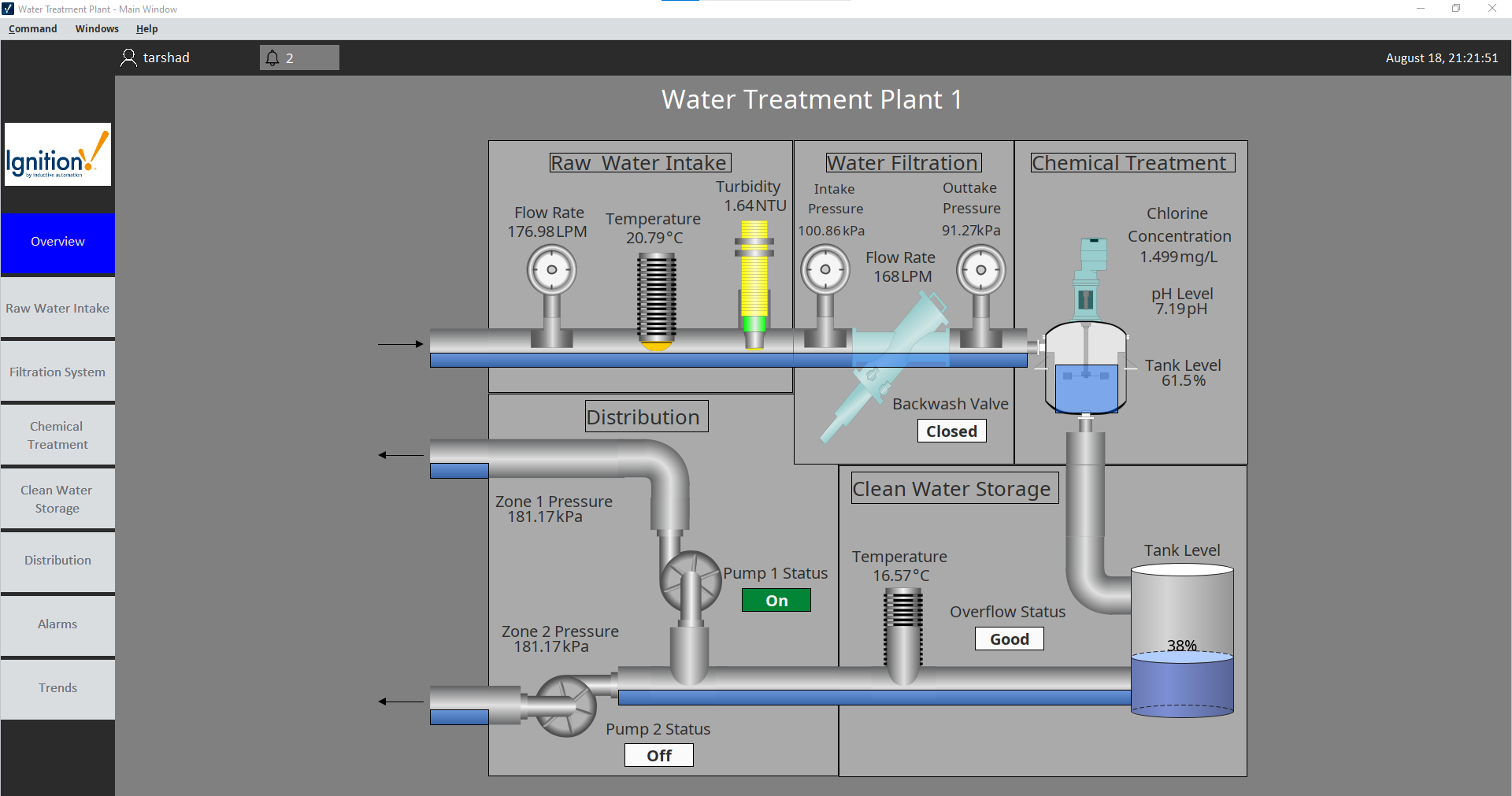
- Raw Water Intake: Flow rate, temperature, turbidity
- Filtration: Pressures, flow, backwash valve status
- Chemical Treatment: Chlorine concentration, pH, tank level
- Clean Water Storage: Tank level, temperature, overflow alarm
- Distribution: Pump statuses, zone pressures, backup generator
Each variable updates in real time, simulating realistic plant behavior. Here’s a snippet from the script:
# Simulate realistic changes
def simulate_realistic(prev, target_range, max_change):
target = uniform(*target_range)
delta = target - prev
change = max(min(delta, max_change), -max_change)
return prev + change
# Example: Update flow rate
vals["raw_flow"] = simulate_realistic(vals["raw_flow"], (160, 200), 1.5)
raw_flow.set_value(round(vals["raw_flow"], 2))Main Screen

Raw Intake Tab
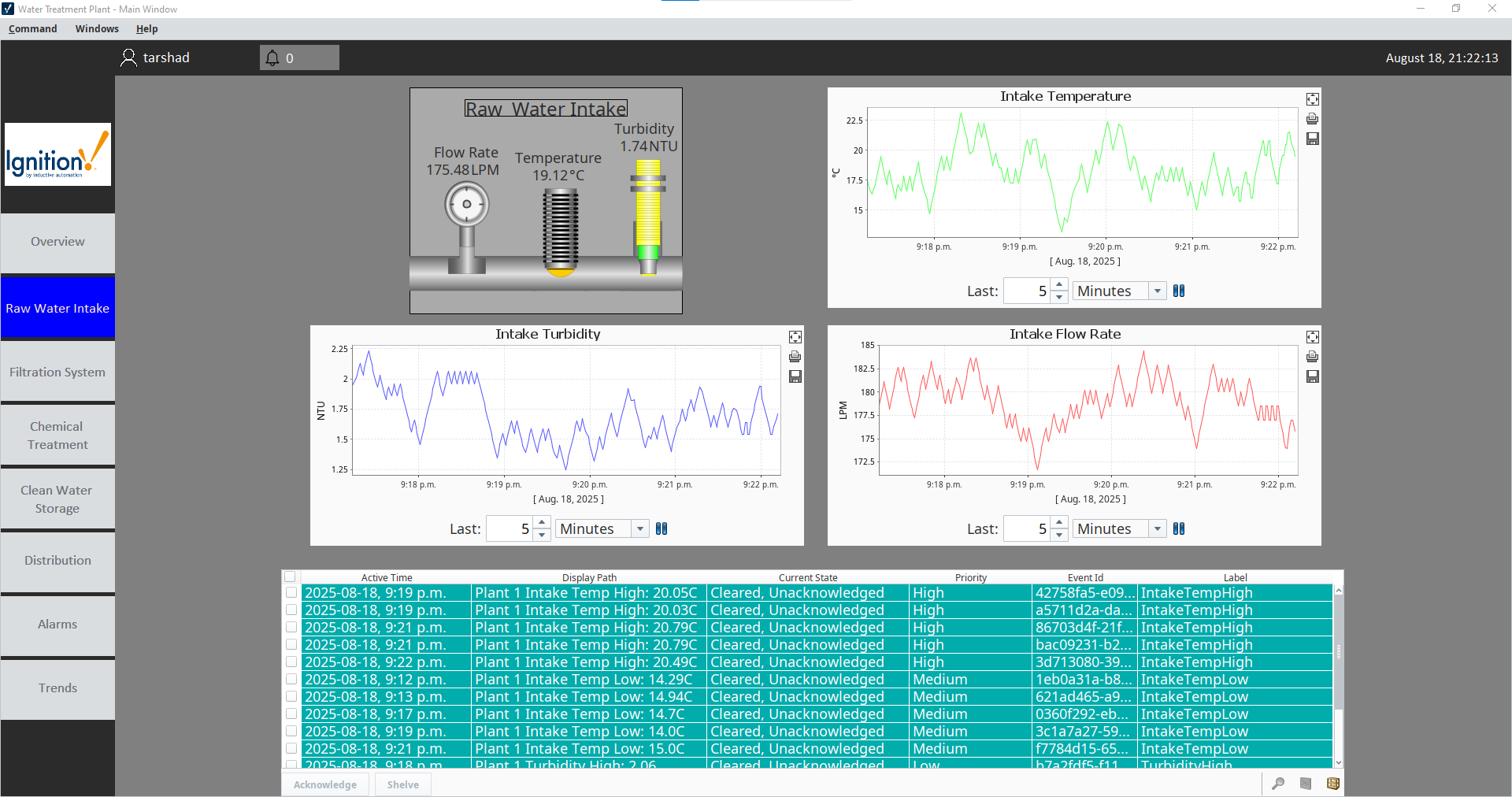
This tab focuses on the raw water intake process, displaying live data such as flow rate, temperature, and turbidity. It’s a great example of how Ignition can visualize and organize process data.
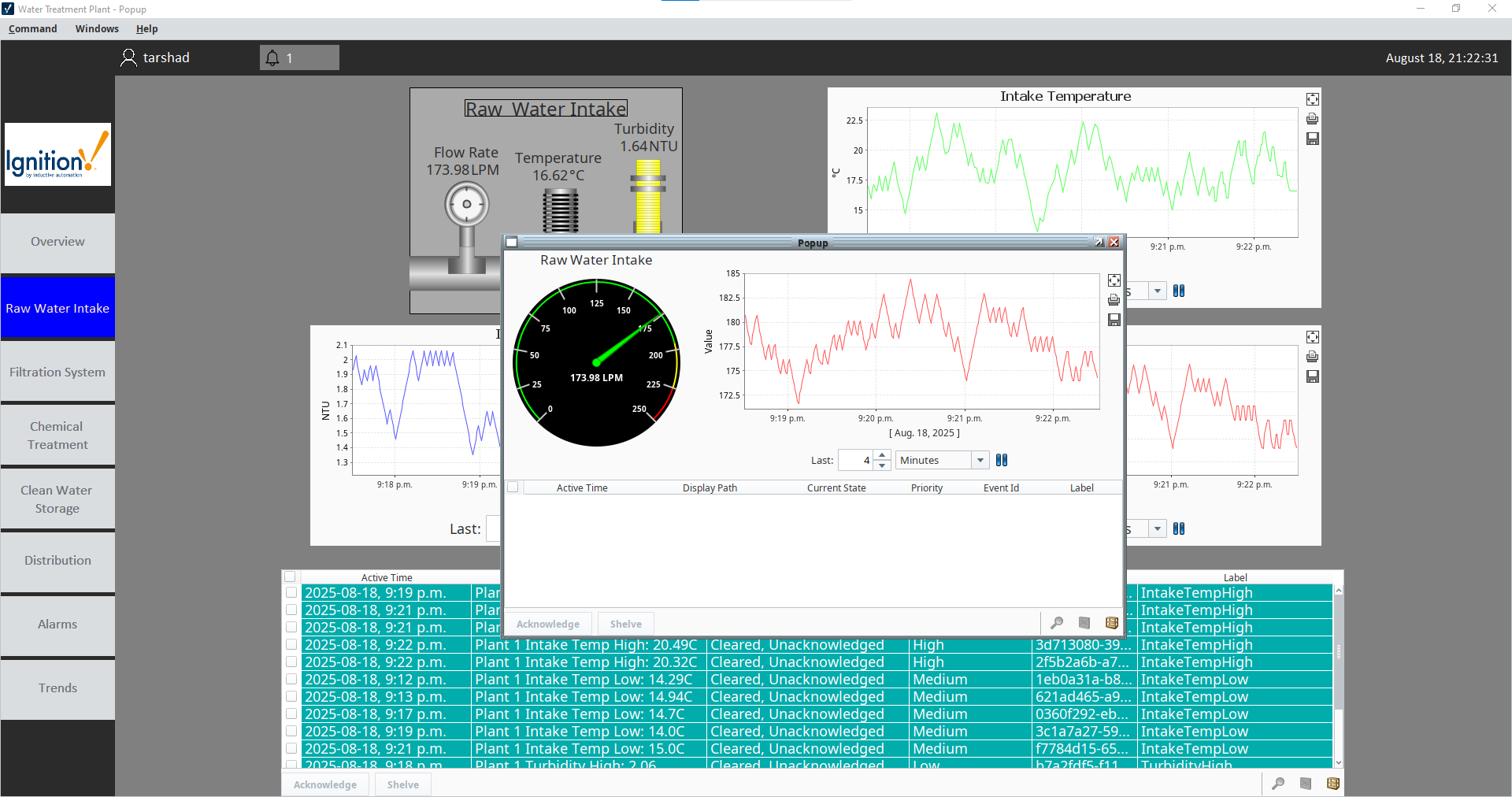
Detailed Raw Flow Information
Simulating OPC UA Data with Python
To power the dashboards, I wrote a Python script that acts as an OPC UA server. It simulates realistic changes in plant variables, including flow rates, pressures, chemical concentrations, and equipment statuses. This approach made it easy to test Ignition’s features and build out the plant logic.
Full Python Code
You can find the complete Python simulation code at the end of this post. Feel free to use or adapt it for your own learning or prototyping!
Reflections
Ignition has proven to be an intuitive and flexible platform for SCADA development. Connecting to OPC UA data was seamless, and the ability to quickly build interactive screens made the learning process enjoyable. I’m excited to keep growing my skills and exploring more advanced features.
For more details and ongoing updates, check out my blog!
Below: Full Python code for the OPC UA simulator.